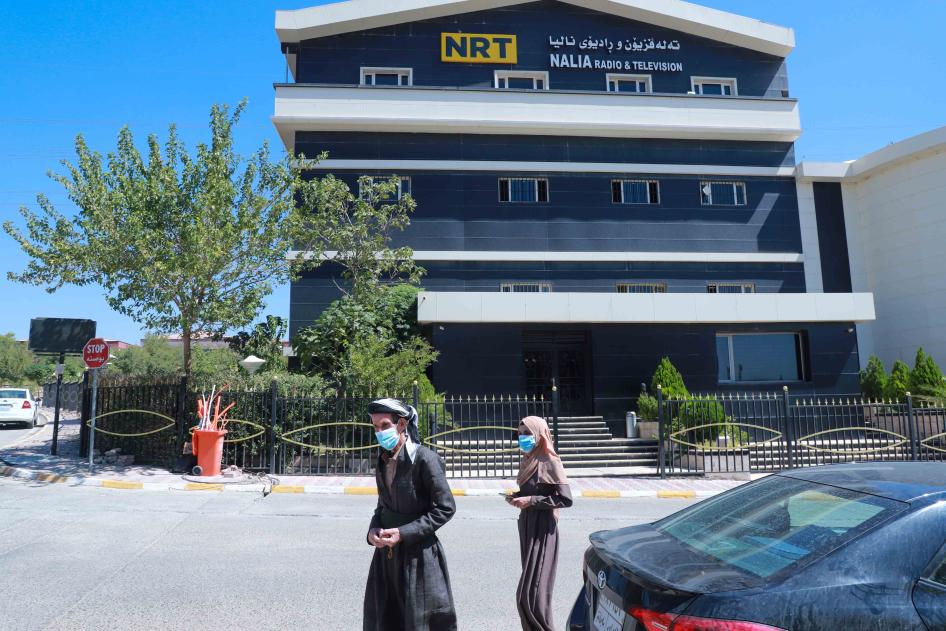
(Beirut) – Kurdish authorities have unlawfully closed two offices of a private media outlet, NRT, for over a month, apparently for covering protests and for broadcasts critical of the ruling party, Human Rights Watch said today.
The Kurdish authorities had no court order and only imposed the shutdown in Erbil and Dohuk, the areas controlled by the Kurdistan Democratic Party, raising concerns that the closure is politically motivated.
“If NRT broke the law, surely the authorities would have taken the appropriate measures to take the outlet to court,” said Belkis Wille, senior crisis and conflict researcher at Human Rights Watch. “But party officials have instead chosen to take actions outside of the scope of the law.”
The harassment of NRT and its reporters follows a pattern of regional government attacks on the media. In June, Human Rights Watch published a report on the range of defamation and incitement legal provisions that Baghdad and Kurdish regional authorities have used against critics, including journalists, activists, and other dissenting voices.
On August 11, 2020, Shaswar Abdulwahid Qadir, the leader of the opposition New Generation Movement political party in the Kurdish Region, issued a call on NRT, a private media outlet with TV and radio stations and a website that he owns, for public protests to demand better education, employment opportunities, and anti-corruption measures. On August 12, his call triggered protests across the region that lasted for about a week. NRT, which has both Kurdish and Arabic language channels, was the only outlet to cover the protests in any detail.
On August 19, NRT’s news director, Rebwar Abd al-Rahman, and another employee who was there told Human Rights Watch that the Asayish – the regional government’s security forces – raided their office in Dohuk and held the staff there for several hours, then ordered them to go home, seemingly in response to the protest coverage.
Al-Rahman said the security forces did not present a court order but said that they had instructions from a Kurdistan Democratic Party official to close down the offices. Al-Rahman said the Asayish also closed their Erbil offices on the same day, again without presenting any court documents. The offices have remained shut, though the channel has remained on the air as authorities did not close its headquarters in Sulaymaniyah down. This has meant that reporting teams in Dohuk and Erbil have been unable to report from the field and appear on TV spots.
Dindar Zebari, the regional government’s coordinator for international advocacy, alleged in a statement to Human Rights Watch on August 23 that NRT and Qadir “consistently aimed to exploit the freedom media agencies enjoy in [the KRI] for their own political agenda … they usually resort to provocative propaganda campaigns amid critical circumstances, such as during the war against terrorism and coronavirus outbreak.”
He said the outlet had violated article 2 of Law No. 12 (2010), which he said makes it a crime for a media outlet to encourage “public disturbance and harm social harmony.” The law allows the Youth and Culture Ministry to close the outlet for 72 hours as an initial penalty, then one week if the violation continues, and finally to withdraw the outlet’s license, he said.
Zebari said that in this case the attorney general had called for suspending NRT’s broadcasts for “encouraging citizens to violate the preventative and social-distancing measures issued by the government,” at the request of the ministry. Human Rights Watch was unable to determine which law Zebari was referring to, given that the law he cited relates to the regional government’s Municipalities and Tourism Ministry.
Zebari said the Youth and Culture Ministry had issued several warnings to NRT, most recently on June 3. However, the head of the Youth and Culture Ministry, Shirwan Aula, said on September 8 his ministry had issued no warnings. On September 9, Zebari accused NRT in a Facebook post of “inciting people to protest and rebel against authority … NRT is always violating the laws by provoking protests and public disorder,” and said that the outlet would be charged under the regional government’s Press Law.
One of NRT’s lawyers, who asked to remain anonymous, told Human Rights Watch on September 17 that the authorities had not sent the company any official warnings or summons to court. He said another lawyer had gone to the Erbil courthouse to confirm whether any legal suits were pending against the company but that court authorities said there were none.
Al-Rahman and the lawyer pointed out that NRT’s headquarters in Sulaymaniyah had not been closed down, which they said indicates that the decision to close the Erbil and Dohuk offices was political, as those governorates are controlled by the Kurdistan Democratic Party, while Sulaymaniyah is not. A court-ordered closing would have to apply throughout the region, including in Sulaymaniyah.
The authorities have taken other measures to intimidate NRT’s staff. On August 19, the Asayish arrested an NRT reporter in Zakho under the KRI’s Law for the Organization of Demonstrations (11/2010), which prohibits people from participating in protests for which the organizers have not sought advanced permission from authorities.
They held him for 11 days, then released him on bail and later dropped the charges, acknowledging he had been covering the protests as a journalist, al-Rahman, the news director, said. He said they also confiscated video equipment of two other reporting teams in Akre, one as a team passed through a checkpoint to report on a Turkish airstrike and the other at a checkpoint outside of Amadiya.
While international human rights law allows governments to place restrictions on the media for national security reasons, these restrictions must be prescribed by legislation and be “necessary in a democratic society.” Any limitation must respond to a pressing public need and be compatible with the basic democratic values of pluralism and tolerance. Restrictions must also be proportionate – that is, balanced against the specific need for the restriction.
Restrictions may not be used to suppress or withhold information of legitimate public interest not harmful to national security, or to prosecute journalists for reporting such information. For the government to fulfill this responsibility, journalists should be able to report on all viewpoints, including those which are in conflict with authorities, without fear of arrest.
Authorities should immediately allow NRT to reopen its offices, and refrain from further acts of intimidation.
“The Kurdistan government has no right to silence coverage of protesters and their demands,” Wille said. “And it definitely does not have the right to shut down an entire outlet, illegally, just for covering protests.”
|
News Release
Kurdistan Region of Iraq: Media Offices Shut Down
Unlawful Action Allegedly Politically Motivated
Your tax deductible gift can help stop human rights violations and save lives around the world.
Region / Country
Topic
Most Viewed
-
December 15, 2024
Sudan: Fighters Rape Women and Girls, Hold Sex Slaves

-
April 22, 2025
UAE: Dissidents, Relatives Designated ‘Terrorists’

-
November 8, 2017
“Everyone Blames Me”

-
August 29, 2024
South Korea’s Digital Sex Crime Deepfake Crisis

-
March 20, 2025
Human Rights Watch declaration on prison conditions in El Salvador for the J.G.G. v. Trump case